Mechanisms – Bar Linkages
29 พฤษภาคม 2566
ผู้ชม 481 ผู้ชม
DESCRIPTION
The Engineering Fundamentals range enables students to gain an understanding of the principles of engineering by the process of learning via experimentation.
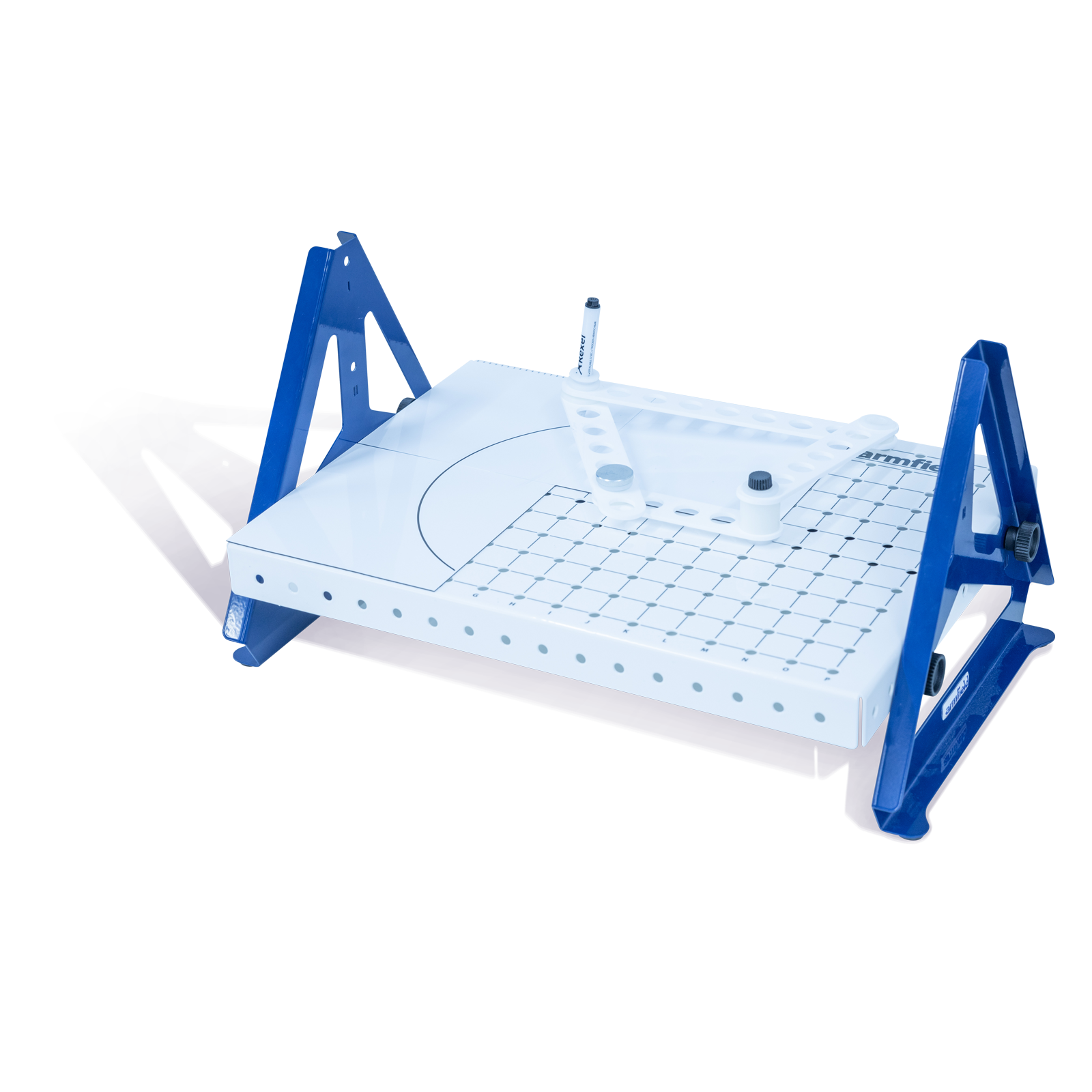
The EF-3.4 Bar Linkages experiments kit comprises of different bars or links configured into a range of different linkage mechanisms, including four-bar linkages, rotary and linear movement and planar linkages allowing students to trace the relative movements of each linkage and joint.
A linkage is an assembly of links and joints that provide a desired output motion in response to a specified input motion.
One such example and one of the simplest moveable closed-chain linkages is the four-bar which consists of four bars or links connected in a loop by four joints and can be used for many mechanical purposes including converting rotational motion to reciprocating motion and converting reciprocation motion to rotational motion.
EXPERIMENTAL CONTENT
- Four-bar linkages – crank rocker, double rocker, drag link and parallelogram
- Determine degrees of freedom of a four-bar linkage
- Straight line linkages – Watt’s straight line, Chebyshev, Peaucellier- Lipkin, Hart’s inversor and Hoeken’s
- The different ways motion is transferred from one motion to another. For example, linear to rotary and linear to rocking
- The different motions scribed by different locations on a bar linkage system
- What is meant by constrained motion?
- Pantograph
- Ackermann steering
Features
- Neatly presented in an easily identifiable and durable storage tray
- Trays have clear lids making it easy to see their contents
- Pictorial tray contents list to identify missing components easily
- Accompanied by a detailed manual with various practical exercises
- Clear and concise assembly instructions for each experiment
- Multiple experiments per kit
- Toolless assembly
Benefits
- Hands-on understanding from lessons
- Improve the student’s dexterity by self-assembly with the instructions provided







