Nanoparticle Size and Zeta Potential Analyzer
08 มีนาคม 2566
ผู้ชม 208 ผู้ชม
The BeNano 90 Zeta is the latest generation of nanoparticle size and zeta potential analyzer designed by Bettersize Instruments Ltd. Dynamic light scattering (DLS), electrophoretic light scattering (ELS) and static light scattering (SLS) are integrated in the system to provide accurate measurements on particle size, zeta potential and molecular weight. The BeNano 90 Zeta is widely applied in academic and manufacturing processes of various fields including chemistry, chemical engineering, biology, pharmaceuticals, food, materials, et cetera.
1) Rapid Measurement Capability
Faster operations and editable results
2) High-performance Solid-state laser
High power semiconductor laser with high beam quality and long service life.
3) Intelligent Intensity Adjustment
Intelligent adjustment of the intensity according to the signal-noise ratio
4) Sensitive Optical Fiber Detection System
Effectively increase signal-noise ratios due to high sensitivity of the optical system
5) Phase Analysis Light Scattering
Measurement of low electrophoretic mobility and zeta potential
6) Disposable Folded Capillary Cell
Excellent repeatability of zeta potential measurements and avoids cross-contamination
7) Capillary Sizing Cell
Sample volume down to 3-5μL and higher measurement accuracy for large particles
8) Intelligent Algorithm of Result Evaluation
Intelligent evaluation and processing of signal quality to eliminate the effect of random events
9) Wide Range of Temperature Control
Adjustable temperature between -10°C and 110°C to meet various measurement requirements and allow thermal stability analysis of samples
10) Highly Stable Optical Design
Provides highly repeatable results, with no routine maintenance required
11) Versatile Calculation Modes
Various built-in calculation modes to cover multiple scientific research and application fields
Features

Dynamic light scattering (DLS), also known as photon correlation spectroscopy (PCS) or quasi-elastic light scattering (QELS), is a technology used to detect the fluctuations of the scattering intensities caused by the Brownian motion of particles.


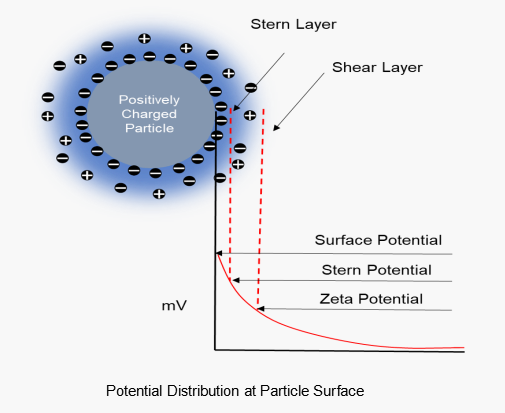
Particles usually carry charges on the surface in aqueous systems, surrounded by counter-ions that form a firmly inner Stern layer and an outer shear layer. Zeta potential is the electrical potential at the interface of the shear layer. Suspension systems with higher zeta potentials tend to be more stable and less likely to form aggregates.
Electrophoretic light scattering (ELS) is a technology for measuring electrophoretic mobility via Doppler shifts of the scattered light. When an incident light illuminates dispersed particles that are subjected to an applied electric field, the frequency of the particles’ scattered light will be different from the incident light due to the Doppler effect. The frequency shift is measured and converted to provide the electrophoretic mobility and hence the zeta potential of a sample by Henry’s equation.
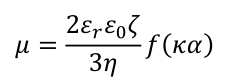
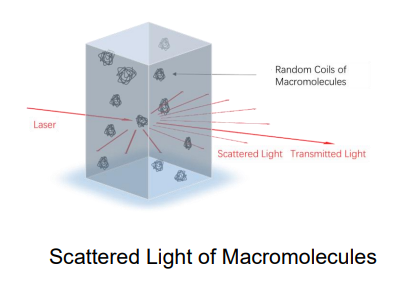
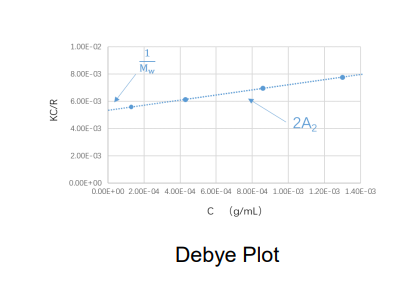
Static light scattering (SLS) is a technology which measures the scattering intensities of the sample, weight-average molecular weight (Mw) and second virial coefficient A2 through Rayleigh equation:
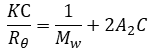
During molecular weight measurements, scattering intensities of the sample at different concentrations are detected. By using the scattering intensity and Rayleigh ratio of a known standard (such as toluene), the Rayleigh ratios of samples at different concentrations are computed and plotted into a Debye plot. The molecular weight and the second virial coefficient are then obtained through the intercept and slope from the linear regression of the Debye plot.